Data Exploration Tool Helps Policymakers Analyze Pre- and Post-Pandemic Student Enrollment Patterns
In the 2020-21 school year, public K-12 student enrollment dropped by 3% nationwide, compared with 2019-20, the school year that marks the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. But this played out differently by state, district, and school among student groups. The COVID-19 and Equity in Education (CEE) Enrollment Explorer is a new interactive data tool designed by the American Institutes for Research (AIR) to help policymakers and educators analyze pre- and post-pandemic student enrollment trends at the state, region, district and school levels, sortable by a range of school, community, and student characteristics.
Key Findings Across Six Key States
The CEE Enrollment Explorer provides enrollment trends about how states, districts, and communities—especially those with high percentages of students who are Black, Latino or experience poverty—responded to the COVID-19 pandemic. A deeper dive into six states—California, Florida, New York, Tennessee, Texas, and Washington—reveals key information about changing enrollment patterns. All six states experienced an overall decline in public school student enrollment since the pandemic onset. Other findings include:
- For Black students, enrollment decline was greatest in California (-8%), New York (-7.6%), and Tennessee (-6.2%);
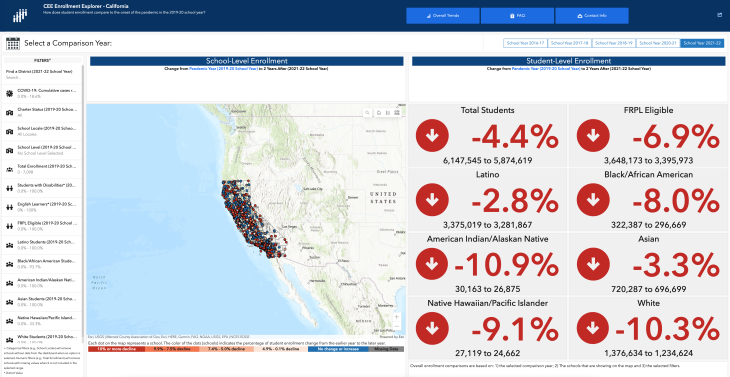
- Declines in enrollment were greatest for white students in California (-10.3%) and Washington (-10.2%);
- Enrollment among students eligible for free and reduced priced lunch (FRPL) declined the most for students in California (-6.9%), New York (-6.9%), and Washington (-8.4%); and
- In all states, enrollment changes among Latino students were minimal, but increased in Florida and Tennessee.
CEE Enrollment Explorer—California
Key data points from the CEE Enrollment Explorer—California include:

- Student enrollment in California declined in both traditional and charter schools, compared with the COVID-19 pandemic onset in 2019-20. However, the decline was smaller in charter schools;
- California schools located in urban areas experienced a 6.2% decline in enrollment since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, larger than the 4.4% decline in enrollment statewide; and
- California schools reported declines in enrollment since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic among students who were eligible for FRPL (-6.9%), Black students (-8.0%), Latino students (-2.8%), and White students.
The CEE Enrollment Explorer—Florida
Key data points from the CEE Enrollment Explorer—Florida include:

- In 2021-22, Florida public school student enrollment declined by 9% compared to enrollment at the onset of the pandemic (2019-20). Enrollment of Latino students increased (1.8%) since the pandemic onset; and
- Florida charter schools showed an overall increase in charter school enrollment (6.2%) compared to the onset of the pandemic (2019-20). Groups with the largest increases in enrollment include students eligible for FRPL (15.3%) and Latino students (9.9%).
The CEE Enrollment Explorer—New York
Key data points from the CEE Enrollment Explorer—New York include:

- In 2021-22, New York public school student enrollment declined by 5% compared to enrollment at the pandemic’s onset (2019-20). In 2021-22 the enrollment of student groups declined among Black (-7.6%), Latino (-2.5%), and White (-7.1 %) students. Among students eligible for FRPL there was a 6.9% decline in enrollment since the pandemic onset – outpacing the overall enrollment decline; and
- New York charter schools showed an overall increase in enrollment (7.5%) compared to the COVID-19 pandemic onset (2019-20). The student groups with the largest increases in enrollment include Black students (11%) and students eligible for FRPL (7.3%).
CEE enrollment explorers are also available for Tennessee, Texas, and Washington. Additional, state-specific dashboards focusing on student performance data and student graduation rate data will be available later this year. View all CEE Enrollment Explorer Dashboards.
About the COVID-19 and Equity in Education: Longitudinal Deep Dive Project
The COVID-19 and Equity in Education: Longitudinal Deep Dive project is jointly funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the AIR Equity Initiative. This work provides a broad, in-depth view of how states, districts, and their communities—especially those with higher percentages of Black and Latino students and/or students experiencing poverty—responded to the pandemic's effect on K-12 learning opportunities. The aim is to understand not just community responses to the pandemic, but how the pandemic has changed core assumptions about how the education system operates in the context of community.